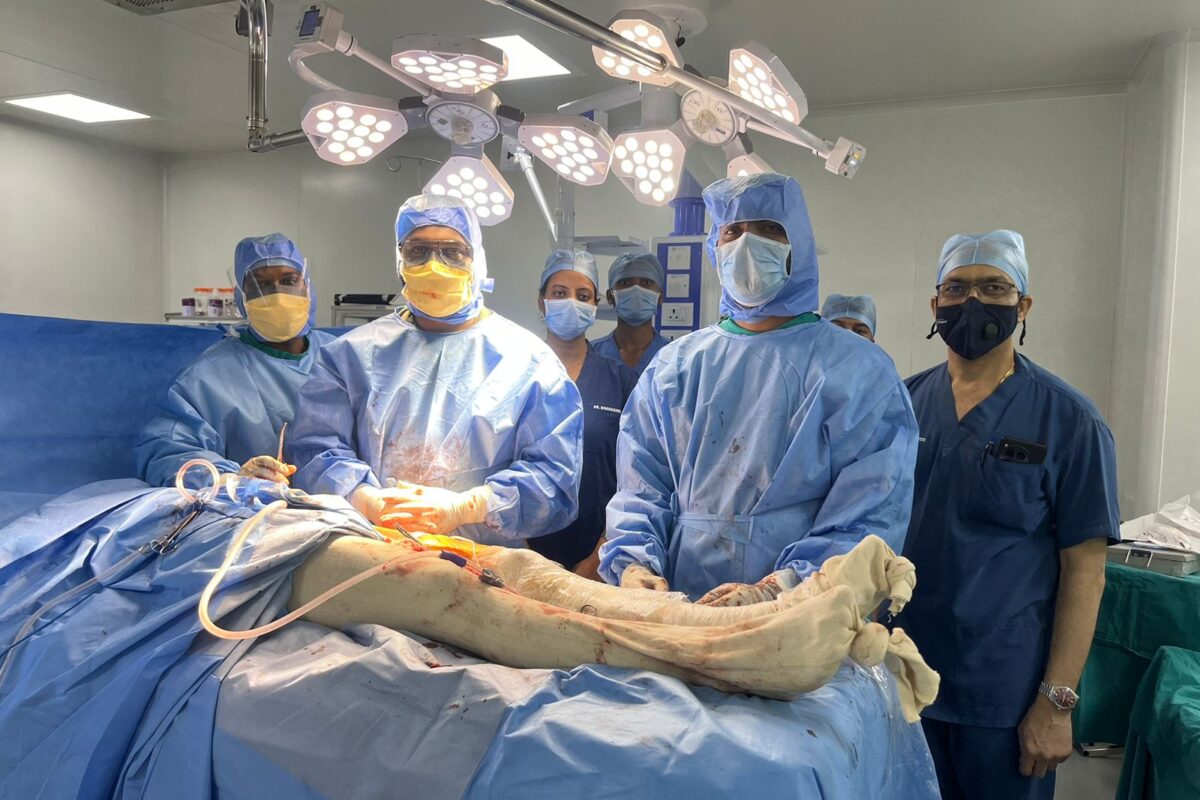
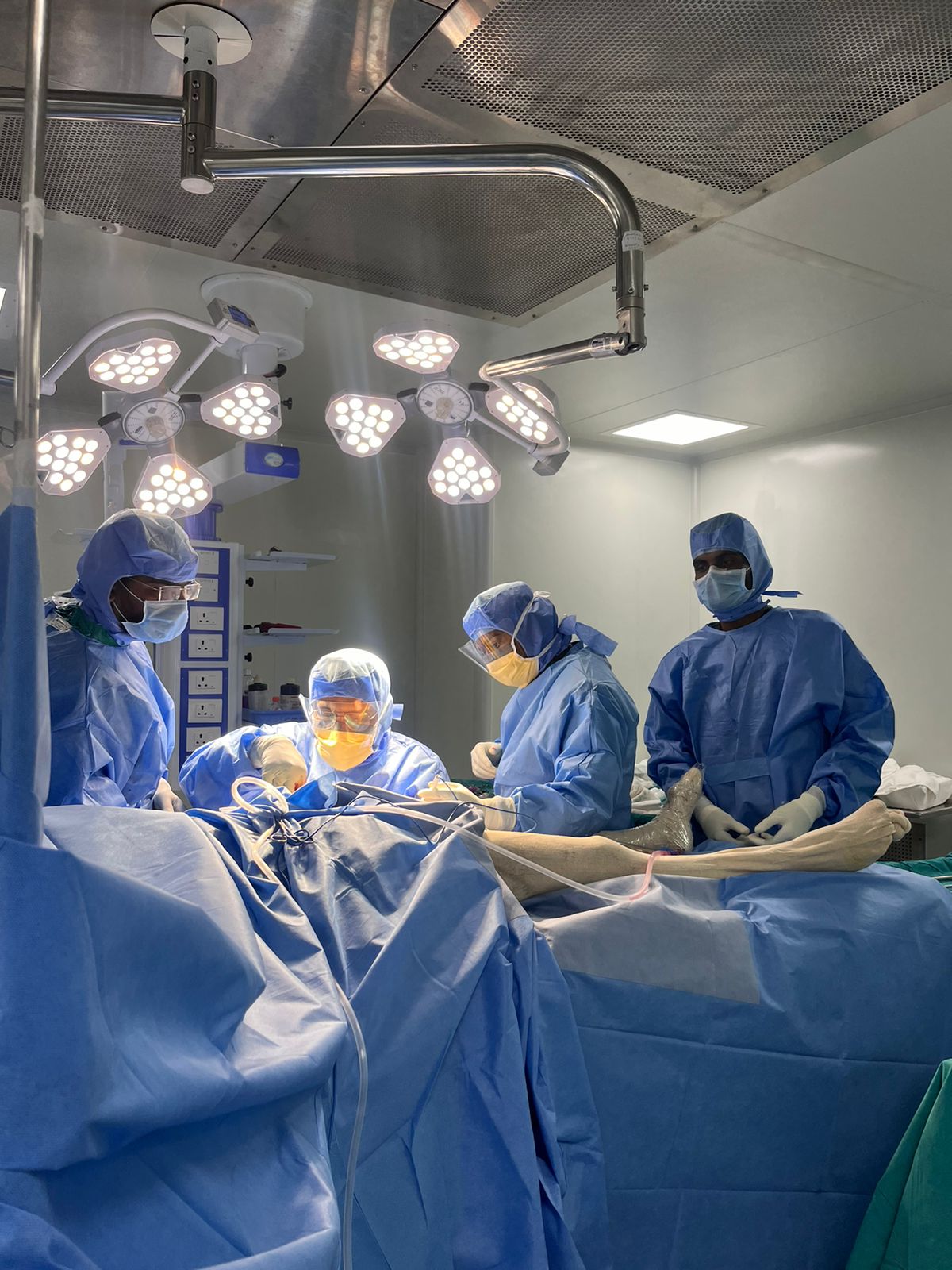
In a remarkable medical achievement, Dr. V.N. Deshpande at Saideep Sahyadri Hospital, Ahilyanagar, successfully performed a femoral neck fracture surgery with augmentation on an 85-year-old patient. This advanced procedure is specifically designed for elderly individuals with fragile bones, offering them a faster recovery and improved mobility.
What is a Femoral Neck Fracture?
The femoral neck is the region just below the ball of the hip joint. A fracture in this area is common among elderly individuals, especially those with osteoporosis (weak bones). Such fractures can lead to severe pain, inability to walk, and complications if not treated promptly.
How Was the Surgery Performed?
Dr. Deshpande utilized augmentation techniques, which involve reinforcing the fractured bone with specialized implants or bone cement. The procedure typically includes:
- Minimally Invasive Approach – Small incisions reduce trauma and blood loss.
- Internal Fixation with Augmentation – Screws, plates, or nails are used to stabilize the fracture, along with bone-strengthening materials like cement or biological agents.
- Quick Recovery – The patient can often bear weight sooner than with traditional methods.

Benefits of Femoral Neck Fracture Augmentation
Faster Healing – Enhanced bone stability promotes quicker recovery.
Reduced Complications – Lower risk of implant failure or re-fracture.
Early Mobility – Patients can start walking with support sooner, preventing bedridden complications like pneumonia or blood clots.
Ideal for Elderly Patients – Designed for those with weak bones who may not tolerate major surgeries well.
Patient’s Recovery & Testimonial
The 89-year-old patient is now on the path to recovery, with physiotherapy aiding in regaining strength and mobility. The family expressed deep gratitude to Dr. V.N. Deshpande and the Saideep Sahyadri Hospital team for their expertise and compassionate care.
Why Choose Saideep Sahyadri Hospital?
🏥 Expert Orthopaedic Team – Led by Dr. V.N. Deshpande, specializing in geriatric fractures.
🏥 Advanced Surgical Techniques – Minimally invasive procedures for better outcomes.
🏥 Patient-Centric Care – Focus on rapid recovery and pain management.